
Table of Contents
What is Nepal’s Health Insurance Program?
- Government Initiative: A social health security program created by the Nepal Government to protect citizens from financial hardship due to healthcare costs
- Management Evolution: Originally under the Social Health Development Committee (2072/073), now managed by the Health Insurance Board (HIB) since 2074/75
- Legal Framework: Operates according to the Health Insurance Act and Regulation
- Financial Protection: Prevents families from falling into poverty due to medical expenses
- Quality Focus: Pushes healthcare providers to deliver better, more accountable services
- Universal Coverage Goal : Works to remove barriers for vulnerable groups and expand healthcare access nationwide
Main Objectices (Health Insurance policy 2013)
- Ensure universal health coverage by increasing access to quality health services.
- Specific objectives
- Enhance financial protection through pre-payment and risk pooling.
- Mobilize financial resources equitably.
- Improve effectiveness, efficiency, accountability, and quality of health care services.
Coverage of health Insurance program (Annual report 79/80)

Cumulative Coverage tabble of health Insurance

Ambitious Targets for Nepal’s Future
- Nationwide Reach: Expansion to all 753 local levels (targeted by 2022)
- Growing Enrollment: Goal of 50% family enrollment during FY 2079/80
- Complete Coverage: Aiming for all families to be covered by 2030
- Reduced Personal Spending: Working to lower out-of-pocket healthcare costs for all Nepalis
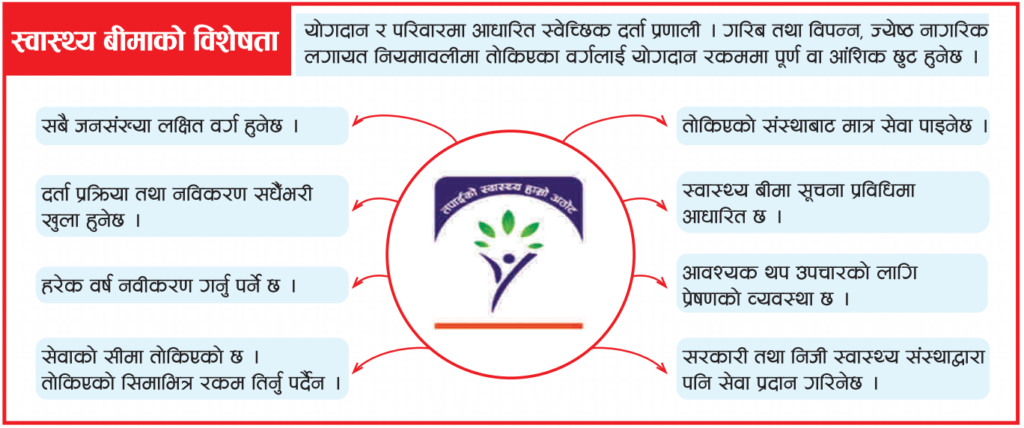
How the Health Insurance Program Works – Simple Breakdown
- Family-Based System: Voluntary program focusing on family enrollment rather than individuals
- Affordable Contribution: NPR 3,500 yearly for families up to 5 members, with NPR 700 for each additional member
- Government Support: Covers costs for seniors over 70, people with specific health conditions (TB, Leprosy, HIV/AIDS), persons with disabilities, and ultra-poor citizens
- Substantial Benefits: Coverage up to NPR 100,000 per year for a family of five
- Additional Coverage: Extra NPR 20,000 for each additional family member
- Maximum Protection: Benefits capped at NPR 200,000 annually based on family size
- Primary Care Model: Members choose their main healthcare facility, with referrals for specialized care
- Cashless Convenience: No need to pay at the point of service
- Tech-Enabled: Uses smartphone technology for enrollment with dedicated local assistants
- Equal Rates: Same payment rates for both public and private hospitals
Impressive Implementation Progress
- Starting Point: Launched in Kailali district on Chaitra 25, 2072
- Early Expansion: Added Illam and Baglung districts in FY 2073/74
- Midpoint Progress: Reached 58 districts by the end of FY 2076/77
- Current Coverage: Now implemented in all 77 districts and 746 local levels across Nepal
Why Health Insurance Matters for Your Family
The Health Insurance Program provides a safety net that protects your family’s finances while ensuring access to quality healthcare when you need it most. With the government’s continued expansion efforts, more Nepalis than ever can benefit from this important program.
Have you enrolled in Nepal’s Health Insurance Program yet? Share your experience in the comments below!
SWOT Analysis of the National Health Insurance Program of Nepal
A SWOT analysis evaluates the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with the National Health Insurance Policy in Nepal. This framework helps to understand the policy’s potential impact and areas for improvement.
Strengths
- Universal Health Coverage Objective: The policy aims to ensure universal health coverage, which is essential for improving health outcomes and reducing inequalities in access to health services .
- Financial Protection: By promoting pre-payment and risk pooling, the policy seeks to enhance financial protection for the public, reducing the burden of out-of-pocket expenses that many households currently face .
- Integrated Health Systems: The emphasis on strengthening health systems in an integrated manner can lead to improved efficiency and accountability in health service delivery .
- Awareness and Behavior Change: The policy includes initiatives to improve health-seeking behavior through awareness-raising, which can encourage more people to utilize available health services .
Weaknesses
- Implementation Challenges: The absence of a national health insurance program until now indicates significant challenges in implementation, which may hinder the policy’s effectiveness .
- High Out-of-Pocket Costs: The current health financing system limits the government’s ability to motivate health care providers, leading to high out-of-pocket expenses that contradict the policy’s goal of financial protection .
- Limited Government Capacity: The government’s capacity to generate sufficient resources for health care is limited, which may affect the policy’s ability to achieve its objectives .
- Risk of Low Enrollment: There are concerns about low initial enrollment in the insurance program, which could undermine the policy’s goals and effectiveness .
Opportunities
- Increased Investment in Health: The policy can attract more investment in the health sector, improving infrastructure and service delivery.
- Partnerships with NGOs and Private Sector: Collaborating with non-governmental organizations and the private sector can enhance service delivery and resource mobilization.
- Technological Advancements: Leveraging technology for health information systems can improve efficiency and accessibility of health services.
Threats
- Political Instability: Political changes and instability can disrupt the implementation of health policies and programs.
- Economic Constraints: Economic downturns may limit government funding for health initiatives, affecting the sustainability of the insurance program.
- Public Resistance: There may be resistance from the public regarding enrollment in the insurance program, particularly if awareness and understanding of the benefits are lacking.
Conclusion
The National Health Insurance Policy in Nepal has the potential to significantly improve health care access and financial protection. However, addressing its weaknesses and threats while leveraging strengths and opportunities will be crucial for its successful implementation and sustainability.
स्वास्थ्य बीमा बोर्ड
links :https://hib.gov.np/en

there are the some area need to be corrected please update this blog